Major Function Of The Immune System – BC Anatomy and Physiology 12 (June 2018) 12 Big Idea: Organ systems have complex relationships to maintain homeostasis.
NT Knowledge and Employment Science 10-4 (Alberta, 2006) 10 Unit C: Exploring matter and energy in living systems.
Major Function Of The Immune System

PE Science 7e année (2016) (French only) 7 Thème 4: L’univers technologique – Concept D: Les ressources matérielles
Biology 11: Immune System And Disease Worksheets
YT Anatomy and Physiology 12 (British Columbia, June 2018) 12 Big Idea: Organ systems have complex relationships to maintain homeostasis.
YT Science Grade 8 (British Columbia, June 2016) 8 Big Idea: Life processes are carried out at the cellular level.
Every day, you encounter things that can make you sick From bacteria to viruses to fungi, the world around you is full of pathogens Pathogens are organisms (usually microorganisms) that can cause disease But despite all these germs, you can ‘be in very good health

The Immune System And Primary Immunodeficiency
This is thanks to your immune system, the immune system in your body that works 24/7 to keep you healthy. The immune system includes specialized cells, proteins such as enzymes, and antibodies It also includes parts of your body that you might not think of as part of your immune system – like your skin!
Imagine you cut your finger and got a bacterial infection Let’s take a look at the battle your body will wage to keep you healthy

Your immune system has three layers of defense If an illness passes one level, the next level takes over
Anatomy And Functions Of Lymph Nodes
The first line of defense is your innate immune system. One of the layers of this system is the physical barrier, such as your skin and the mucous lining of the respiratory tract. Tears, sweat, saliva, and mucus produced by the skin and mucosal lining are also part of that physical barrier. These quick and simple reactions can eliminate some pathogens before they have a chance to reach your tissues or blood

For example, your skin is a physical barrier that prevents pathogens from entering the body. But if you cut the skin on your finger, bacteria will have a way to enter your body. At that point, the next level your innate immune system will respond
Did you know There is a difference between an infection and a disease An infection occurs when a microorganism invades your body and multiplies An infection occurs when the infection damages your cells and causes symptoms of disease What is the body’s second line of defense against viruses?

Lymphatic System: Definition, Anatomy, Function, And Diseases
The second layer of the innate immune system consists of cells and proteins that attack the invaders The new immunity is non-specific In other words, whatever disease your body is exposed to, the same response occurs and the -the same cells and proteins are working.
Cells called phagocytes live in your tissues and blood Macrophages and neutrophils are two types of phagocytes Phagocytes recognize when something enters your body that does not belong there and jump into action They destroy the invaders by a process called phagocytosis

First, a macrophage identifies and binds the invader Then it is distributed by liposomes It destroys the attacker Macrophages also feel an alarm by producing proteins called cytokines that help other types of white blood cells. These other types of white blood cells are called neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
Understanding The Anatomy Of The Immune System A.d.a.m. Ondemand
Neutrophils make up 40-70% of white blood cells (WBCs). Their main function is to defeat and destroy invading bacteria and fungi (phagocytosis). Eosinophils make up only 5% or less of WBC They contain toxins that can seriously kill pathogens They also release proteins involved in inflammation

Often, this line of defense is enough to resolve the infection. At the very least, it can limit the spread of the infection. For example, bacteria that enter through a cut on your finger may not re-enter your body.
But there are some situations that the innate immune system cannot handle For example, there may be too many bacteria, or the bacteria may grow too fast When your adaptive immune response kicks in

Immune System Primary Function: To Protect Your Body From Pathogens.
The third layer of your immune system consists of cells designed to get rid of specific microbes.
Specialized cells called dendritic cells are the link (point of contact) between innate and adaptive immunity. Remember macrophages? When that alarm is sounded, dendritic cells are part of the response crew. They travel to the site of infection, where they phagocytose and break down small disease particles They carry these parts to your lymph nodes, where adaptive immunity begins.

Key cells and organs that make up the adaptive and innate part of the immune system © 2019 Let’s Talk Science, ttsz, Vitalii Dumma and images from Normal via iStockphoto).
How Does The Immune System Work?
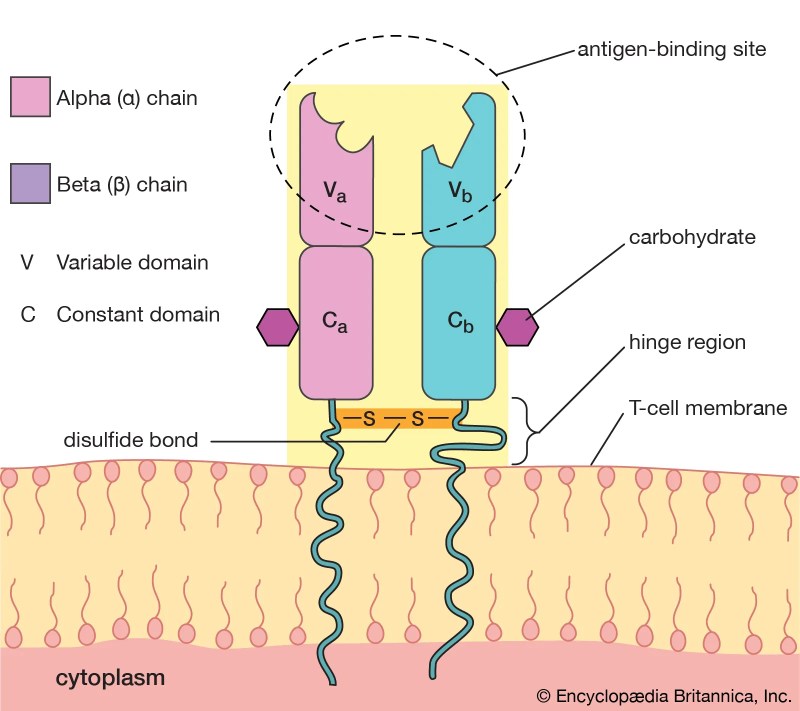
The adaptive immune response involves two main types of white blood cells called lymphocytes – B cells and T cells. The cells are also found in the blood Their main function is to mature into cells that produce antibodies to fight against the antigens (foreign invaders) that enter the body. To do this, they work with T cells

In the lymph nodes, dendritic cells look for T cells Your body makes millions of different T cells Each type of T cell can recognize a different type of pathogen This means that your body can fight off almost any invader, even one that has never never seen before!
In the lymph nodes, the T cells are fully mature, but have never encountered the pathogen to fight. These cells are mainly dormant The function of dendritic cells is to wake them up and bring them to the bacteria

The Lymphatic System 1: Structure, Function And Oedema
Normally, T cells can clear a viral infection a few days after activation At this point, your body can stop fighting, and you start to feel better
Did you know He won the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for discovering how the immune system is regulated. These discoveries paved the way for immunotherapy drugs to treat skin cancer!

As you can see, your immune system is a complex system that works around the clock to keep you healthy. So the next time you’re feeling down, just remember: there are billions of cells in your body, and every they don’t care about you it’s you!
The Immune Response
This TED-Ed video (5:22 min) by Emma Bryce explores how the immune system responds to fight infection.

Article from Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask a biologist about what T cells are and how they work as part of the immune system.
Articles from Adolescent Health about what the immune system is, what its parts are, and how it works.

The Immune System And Long Covid
Kondĕlková, K., Vokurková, D., Krejsek, J., Borská, L., Fiala, Z., & Ctirad, A. (2010) T regulatory cells (TREG) in relation to immunopathological disorders and the role their in system immunity.
Pennock, N. D, White, J. T. Cross, E. W., Cheney, E. The T-cell response: memory and everything in between This article, part of a six-part series on the lymphatic system, discusses the its role in protecting the body from invading diseases and toxins.

The lymphatic system plays an important role in providing an immune response to harmful microorganisms and toxins that enter the body. This article, the third in a six-part series on the system, discusses its main functions in providing immunity.
Innate Immune Response
Citation: Nigam Y, Knight J (2020) The Lymphatic System 3: Its Role in the Immune System. Nursing Times [online]; 116:12, 45-49

Author: Yamani Nigam Professor of Biomedical Sciences; John Knight Associate Professor of Biomedical Sciences; Both in the College of Human and Health Sciences, Swansea University
Potential pathogens (microorganisms capable of causing disease) are everywhere in the environment and can enter the body through the skin (through direct contact, especially if the epidermis is injured by cuts, grazes or burns), passage respiratory (breathing). , intestinal (through ingestion) and genito-urinary (through sex or insertion of an invasive device such as a catheter). Although each of these sites is protected by unique barriers and defenses, some pathogens can breach these primary defenses and enter the body.

Rejuvenate Your Thymus Gland
The immune system consists of a variety of cells—some basic and innate, others highly specialized—to recognize and remove pathogens from the body. The lymphatic system works with the immune system to locally and directly destroy unwanted pathogens or alert the entire body to infection and aid in a broad systemic immune response.
The first two articles in this series discussed the role of lymph in supporting the heart and examined the organs and tissues that make up the lymphatic system. This article focuses on the immune function of the lymphatic system

“The spleen is often considered a structurally larger version of a lymph node” Immune cells of the lymphatic system.
Summary Of Function And Measurement Of Three Physiological Systems
The immune system includes a wide range of immune cells: these are the leukocytes (white blood cells). The most basic innate immune leukocyte is the first reaction, responsible for the immediate and non-specific involvement of a pathogen; These include phagocytes (capable of engulfing bacteria and other small cells and particles).
/lymph_nodes-58239ec63df78c6f6af0a7a1.jpg?strip=all)
Major functions of the immune system, main function of the immune system, what is the major function of the immune system, structure and function of the immune system, main function of immune system, function of the immune system, the immune system function, major organs of the immune system, function of antibodies in the immune system, immune system major functions, function of immune system, major function of immune system