The Study Of Antigen Antibody Reactions Is Known As – Although every effort is made to follow the rules of citation style, some inconsistencies may occur. If you have questions, consult the appropriate style guide or other resources.
Join the Publishing Partner Program and our community of experts to get a global audience for your work!
The Study Of Antigen Antibody Reactions Is Known As

An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance called an antigen. Antibodies recognize antigens and attach to them to remove them from the body. The body recognizes a wide variety of substances as antigens, including disease-causing organisms and toxins such as insect venom.
Solved A 3. The Term Serology Is Used To Describe A Broad
When a foreign substance enters the body, the immune system recognizes it as foreign because the molecules on the surface of the antigen are different from those found in the body. To destroy the invader, the immune system calls upon several mechanisms, the most important of which is the production of antibodies. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the surface of a B cell, it triggers the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone. Mature B cells, called plasma cells, release millions of antibodies into the blood and lymphatic system.

When antibodies circulate, they attack and neutralize antigens that have triggered an immune response. Antibodies bind to antigens and affect them. Binding of an antibody to a toxin, for example, neutralizes the toxin by changing its chemical composition; Such antibodies are called antitoxins. By attaching to certain invasive microbes, other antibodies can immobilize such microbes or prevent them from entering the body’s cells. In other cases, the antibody-coated antigen undergoes a chemical chain reaction with complement on a series of proteins in the blood. The complement response can cause lysis (cleavage) of the invading microbe or recruit scavenger cells that engulf or phagocytose the invader and kill the microbe. Once antibody production begins, it continues for several days until all antigen molecules are destroyed. Antibodies remain in circulation for several months, providing extended immunity against a specific antigen.
Together, B cells and antibodies perform one of the most important functions of the immune system, which is to recognize an invading antigen and produce a host of protective proteins that cleanse the body to remove all traces of that antigen. Normally, B cells recognize an almost infinite number of antigens; However, each B cell binds to only one type of individual antigen. B cells recognize antigens using proteins called antigen receptors found on their surface. An antigen receptor is an antibody protein that is not primarily secreted but attached to the B-cell membrane.

Dynamics Of Sars Cov 2 Neutralising Antibody Responses And Duration Of Immunity: A Longitudinal Study
Medical Terms and Mentors Quiz Who Invented the Basic Blood Groups? What causes the blood disease Thalassemia? Test your knowledge of medical science by taking this quiz.
A bank in Italy accepts cheese as collateral for loans to dairy farmers. Their special warehouses hold over 440,000 giant wheels of Parmigiano-Reggiano.

All the antigen receptors found on a particular B cell are the same, but the receptors found on other B cells are different. Although their general structure is similar, the difference lies in the antigen-interacting region – the site where the antigen binds or binds antibodies. This structural variation between antigen binding sites allows different B cells to recognize different antigens. The antigen receptor does not actually recognize the entire antigen; Instead, it binds to only a portion of the antigen’s surface, a region called the antigenic determinant or epitope. A connection between a receptor and an epitope can only occur if their structures are complementary. If they are, the epitope and receptor fit together like two pieces of a puzzle, a necessary event to activate B-cell production of antibodies. This article is primarily based on one source. Related discussion can be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by including links to additional resources. Find sources: “Agglutination” Biology – News · Newspaper · Books |
Pdf) Precipitation Reactions In Immunology
Agglutination is the process that occurs when an antigen combines with an appropriate antibody called an isoagglutinin. This term is generally used for blood type.

The “bed card” method of determining blood type, in this case, the Serafoll card is used. The result is blood type A positive.
Hemagglutination is the process of aggregation of red blood cells, that is, sticking or clotting. The agglutin involved in hemagglutination is called hemagglutinin. In a cross-match, the donor’s red blood cells and the recipient’s serum or plasma are incubated together. If admixture occurs, it indicates that the blood groups of the donor and recipient are incompatible.

Antibody Binding Epitope Mapping (abmap) Of Hundred Antibodies In A Single Run
When a person produces antibodies against their own red blood cells, such as in cold agglutinin disease and other autoimmune conditions, the cells can self-aggregate.
This is called autoagglutination, and it interferes with laboratory tests such as blood typing and complete blood counts.

Agglutination is commonly used as a method to identify specific antibacterial agents and identify such bacteria and is therefore an important method in diagnosis.
Generation And Functional Characterization Of A Single Chain Variable Fragment (scfv) Of The Anti Fgf2 3f12e7 Monoclonal Antibody
Two bacteriologists Herbert Edward Durham (-1945) and Max von Gruber (1853-1927) discovered the specific combination in 1896. The group is known as the Gruber-Durham reaction. Gruber used the term agglutinin (from Latin) for any substance that causes the aggregation of cells.

French physician Fernand Vidal (1862–1929) later experimented with Gruber and Durham’s discovery in 1896, using the reaction to test for typhoid fever. Vidal found that the serum of a carrier of typhoid caused a culture of typhoid bacteria, while the serum of a person without typhoid did not. This Widal test was the first example of serum diagnostics.
Another important practical application of the addition reaction was discovered in 1900 by the Austrian physician Karl Landsteiner. Landsteiner’s agglutination tests and his discovery of ABO blood groups pioneered the science of transfusion and serology, making transfusion possible and safe. A shaped protein used by the immune system to recognize and neutralize foreign substances such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. An antibody recognizes a specific molecule of a pathogen called an antigen.

Sensing Of Covid 19 Antibodies In Seconds Via Aerosol Jet Printed Three Dimensional Electrodes
At each end of the “Y” end of the antibody, there is a paratope (like a lock) unique to an epitope (similar to a key) on the antigen, allowing the two structures to join with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can recognize or directly neutralize a microbe or infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system (for example, by blocking a part of the virus that is important for its attack).
The antigen-binding sites at both ends of the antibody fall within an equally wide range to allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens. In contrast, the rest of the antibody is relatively stable. It occurs only in certain variants that determine the class or isotype of the antibody: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM. The constant region on the stem of the antibody contains sites that interact with other components of the immune system. The hce class, along with some structural features, defines the function activated by the antibody after binding to the antigen. Different classes of antibodies differ in where they are produced in the body and at what stage of the immune response.

Along with B and T cells, antibodies form the most important part of the adaptive immune system. They exist in two forms: one bound to the B cell and the other insoluble in extracellular fluids such as blood plasma. Initially, all antibodies are in the first form attached to the B-cell surface – this is called the B-cell receptor (BCR). After the antigen binds to the BCR, the B cell is activated to proliferate and differentiate or become plasma cells that produce soluble antibodies of the same paratype or memory B cells that reside in the body for long-term antibody-resistant immunity.
Part 1: Blood Typing Be Sure To Have Read The
Soluble antibodies are released into the blood and tissue fluids, as well as into many secretions. Because these fluids are traditionally called humors, antibody-mediated immunity is sometimes called or considered part of humoral immunity.

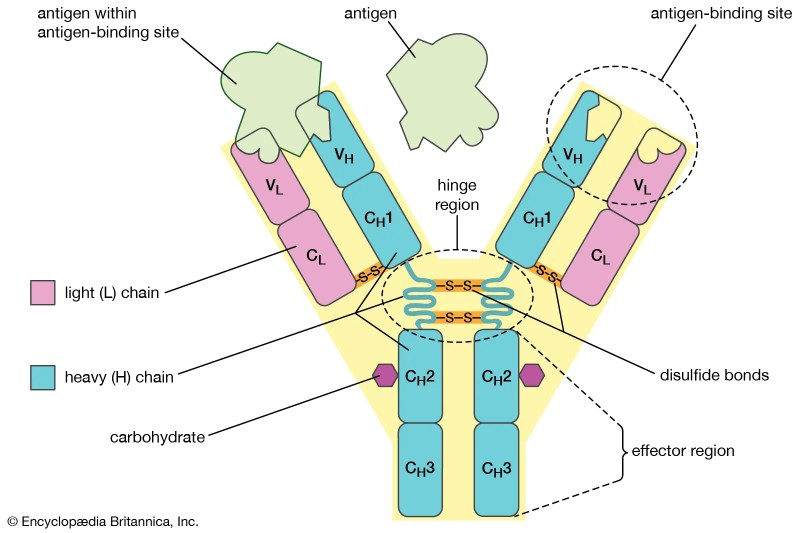
Schematic structure of an antibody: two heavy chains (blue, yellow) and two light chains (grey, pink). The antigen binding site is circled.
A more accurate representation of the antibody (3D structure in the RCSB PDB). Glycans in the Fc region are shown in black.

Single B Cell Technologies For Monoclonal Antibody Discovery: Trends In Immunology
In humans and most mammals, an antibody unit consists of four polypeptide chains; Two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains connected by disulfide bonds.
Each chain is a sequence of domains: somewhat similar sequences of 110 amino acids each. These domains are usually repeated as rectangles in simplified schemes. Light chains have a single variable V domain

Between them is a hinge region of heavy chains whose flexibility allows antibodies to bind to pairs of epitopes at different distances, forming complexes (dimers, trimers, etc.) and binding effector molecules more easily.
Blood Agglutination Grading Study Guide
During the electrophoresis test of blood proteins, mainly antibodies

Study of algae is known as, types of antibody antigen reactions, study of insects is known as, study of coins is known as, antigen antibody reactions, serology is the study of antigen antibody reactions, the antibody therapy known as, study of cell is known as, the study of the immune system is known as, the study of adult learning is known as, study of antigen antibody reactions, study of earthquakes is known as