The Study Of The Immune System Is Known As – The immune system is made up of different cell types and proteins. Each element performs a specific function aimed at recognizing and/or reacting to foreign substances (pathogens).
The immune system is a vast collaboration of cells and proteins that work together to protect against infection. These cells and proteins do not make up a single organ like the heart or liver. Instead, the immune system spreads throughout the body and rapidly responds to infection (Figure 1). The cells travel in the blood or in special vessels called lymphatics. Lymph nodes and spleens provide structures that facilitate cell-to-cell communication. The protein can be made by immune cells or other organs such as the liver. Some immune proteins circulate in the blood, while others are made by immune cells and act on nearby organs and tissues to produce proteins.
The Study Of The Immune System Is Known As
A. Thymus: The thymus is an organ located in the upper chest where T cells mature. First, lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) identified as T cells leave the bone marrow and travel to the thymus, where they are “trained” to become mature T cells.
Immune Response To Sars‐cov‐2 And Mechanisms Of Immunopathological Changes In Covid‐19
B) Liver: The liver is the main organ responsible for the production of complement system specialists. In addition, it has large numbers of phagocyte cells (a special type of white blood cell) that engulf bacteria in the blood as they pass through the liver.

C. Bone marrow: Bone marrow is where all the cells of the immune system develop from stem cells.
E. Lymph nodes: Lymph nodes are B cells and T cells throughout the body. Cells gather in lymph nodes to communicate with each other. Lymph nodes can become swollen as they fight infection.

The Virus Is Evolving. But So Are Your Antibodies.
F. Cell: Sputum is a collection of B cells, T cells, and monocytes. It serves to filter the blood and provides a site for interactions between invaders/microbes and cells of the immune system.
G. Blood: Blood is present in the circulatory system and carries immune system cells and proteins from one part of the body to another.

Primary immunodeficiency disease (PI) can affect one or more cells and proteins of the immune system. To better understand the types of PI, it is useful to understand the regulation and maturation of the immune system. It is common to view the immune response in two broad categories: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
When The Immune Response Makes Covid 19 Worse
Innovative immune responses are those that rely on cells that do not require additional training to perform their functions. These cells include neutrophils, monocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and a set of proteins called complement proteins. Innate responses to infection are rapid and reliable. Even children have natural immune responses.

Adaptive immune responses fall into the second category. These responses include T cells and B cells, two types of cells that must learn to fight invaders (antigens) and not attack our own cells. Advantages of adaptive responses are their long-term memory and ability to adapt to new types of infection.
The bone marrow and thymus represent the training ground for the two cells of the adaptive immune system (B cells and T cells). The development of all cells of the immune system begins with hematopoietic (blood-forming) stem cells in the bone marrow (Figure 1). This cell is called a stem cell because other specialized cells arise from it. Because of its ability to form a complete immune system, the cell is most important in bone marrow or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. It is related to embryonic stem cells, but it is a separate cell type that can develop into any type of blood cell, but not other organs such as the brain or muscles.

Lymphatic System And Immune System
A. Bone marrow: the site where most cells of the body’s immune system develop from hematopoietic stem cells.
B. stem cells: These cells have the ability to grow and reach different cells of the immune system.

D. B cells: These lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow and differentiate into plasma cells, which in turn produce immunoglobulins (antibodies).
The Immune System: Cells, Tissues, Function, And Disease
E. Cytotoxic T cells: These lymphocytes mature in the thymus and kill virus-infected cells.

F. Helper T cells: These specialized lymphocytes help other T cells and B cells perform their functions.
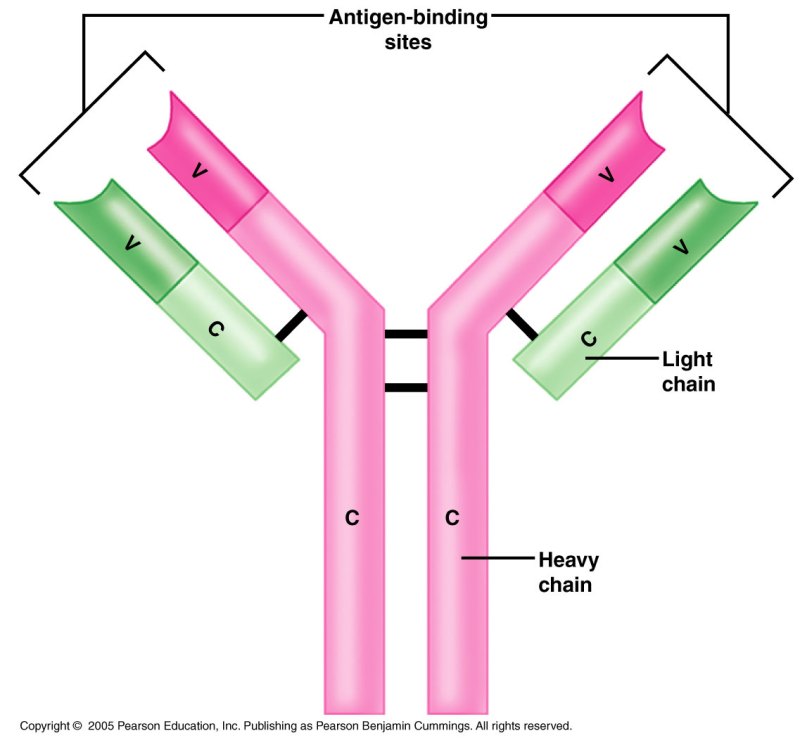
Kh. Immunoglobulins: Also known as antibodies, these highly specialized protein molecules fit like a lock and key against foreign antigens like polio. Their diversity is so wide that they can be produced to suit all the microorganisms in our environment.

Adaptive Immune System
I. Neutrophils: (also called polymorphonuclear cells or PMNs) are a type of white blood cell in the blood that rapidly engulf microorganisms through a process called phagocytosis.
J. Monocytes: These white blood cells are cells in the blood that, when transported to tissues, give rise to cells called macrophages. Like neutrophils, macrophages engulf and kill microbes through phagocytosis.

K. Red blood cells: red blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
Immune System Clock Successfully Predicts Illness And Mortality
Central to both categories of immune responses is the ability to distinguish foreign invaders (pathogens) against our own tissues that must be protected. Because of their ability to react quickly, natural reactions are usually the first to respond to an attack. This initial response serves to prevent and trigger the adaptive response, which may take several days to fully activate.

Natural responses are very important in early life. Newborns have antibodies from their mothers, but don’t make their own for several weeks. Maternal antibodies are transferred to the baby across the placenta and protect the baby for the first few months of life until it makes enough antibodies on its own.
The adaptive immune system is active at birth, but has not received the necessary experience for an optimal memory response. Although this memory formation is lifelong, the most rapid gains in memory experience occur between birth and three years of age. Each infectious exposure trains the cells to respond more quickly and extensively to the same infection a second time.

Proven Ways To Strengthen Your Immune System
During the first few years of life, many children are exposed to various infections and develop antibodies. Antibody-producing B cells remember the infection (pathogen) and provide long-term immunity. Likewise, T cells remind the body of viruses and can mount a stronger response when exposed to the same virus. This rapid development of the adaptive immune system during infancy makes testing young children difficult, as normal changes are expected with age. Unlike the adaptive immune system, the innate immune system is protected at birth.
Each important part of the immune system will be discussed separately. PI can affect one or more parts. Indications may be a specific type of infection or a universal susceptibility to infection. Because of the many interactions between cells and proteins of the immune system, some types of PI are associated with very limited infection. For these forms, there are other elements that can at least cover the missing pieces. In other cases, the immune system is usually very weak, and a person can have serious problems with many different infections.

The most common cells of the immune system can be classified as lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, and NK cells), neutrophils, and monocytes/macrophages. These are all white blood cells. The main proteins of the immune system are mainly cytokines (a type of hormone responsible for communication between immune system cells), antibodies (immunoglobulins) and complement proteins.
A Cheaper Way To Study The Immune System, One Cell At A Time
V. B cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. As part of normal maturation in the bone marrow, B cells are trained, or educated, not to make antibodies against healthy tissue. Once mature, B cells can be found in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, parts of the intestine, and blood.

When B cells are exposed to foreign microbes (antigens), they respond to other cells called plasma cells. B cells can also become memory cells, allowing them to respond more quickly if the same infection occurs again. Plasma cells are mature cells that produce antibodies and are found in the lymph nodes and lymph nodes. Antibodies are highly specific protein molecules that enter the blood, tissues, respiratory tract, intestinal secretions, and even tears. In general, plasma contains cells
Study of cell is known as, the study of tissue is known as, the study of fossils is known as, the study of muscular system is known as, study of earthquakes is known as, the study of adult learning is known as, study of universe is known as, study of insects is known as, the study of antigen antibody reactions is known as, study of the universe is known as, study of algae is known as, study of coins is known as