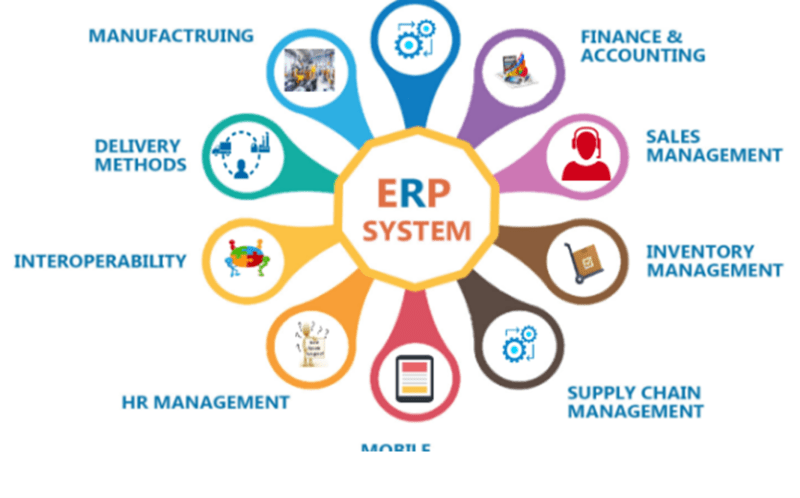
What Erp Stands For – Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software system designed to automate and optimize a company’s core business processes. It provides a unified and streamlined approach to corporate operations by acting as a central hub for data flow between various departments. ERP software has the ability to connect a range of business activities on a single platform, including finance, supply chain, operations, trade, reporting, manufacturing and human resources.
While most companies have financial and operational systems in place, the use of silo systems can limit the scope of day-to-day business processes and hinder future growth. As companies grow, their needs evolve and their systems have to keep up. This article explains the benefits of having an ERP system that can adapt to changing needs and help run a more agile and efficient business.
What Erp Stands For

Although ERP technology does not offer a comprehensive solution for every business process, it is constantly improving its ability to integrate processes. When your processes, systems, and data are connected through ERP, you have access to the necessary business intelligence, acceleration, and scalability needed to optimize your operations.
What To Do About Disparate Erp Systems?
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a cloud-based ERP solution designed specifically for small and medium businesses. It offers a range of functions to help manage core business processes, including financial management, inventory management, sales and purchasing, project management, and customer relationship management. Business Central also includes built-in artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities that help businesses automate routine tasks, make data-driven decisions, and increase overall efficiency. With its cloud-based infrastructure, Business Central enables real-time data access and collaboration between teams and departments, allowing businesses to work more efficiently and make informed decisions. Additionally, Business Central can be easily integrated with other Microsoft products such as Office 365, Power BI and Microsoft Power Platform, giving businesses a comprehensive suite of tools to manage their operations. cut it off. This is where enterprise resource planning software comes in: ERP systems collect and organize critical business information and help organizations run lean, efficient operations even as they expand.
Most business professionals have heard the term “ERP” but may not know exactly what enterprise resource planning systems can do for their teams. We’ll explain exactly what ERP is, how it works, what it can do for your business, how to choose the right solution, and more.
At its core, ERP is an application that automates business processes and provides insight and internal controls, based on a central database that collects input from departments including accounting, manufacturing, supply chain management, sales, marketing, and human resources (HR).
Every business has to do a business that requires a large number of stakeholders with different responsibilities. But it’s a struggle when the information needed to run processes and make important decisions is spread across disjointed systems. Whether data is stored in core business management software or spreadsheets, employees struggle to find what they need and may not have full access to it. For example, accounting and FP&A teams may have different spreadsheets with different numbers to track costs.
Employing Ai/ml In Federal Erp Systems
These disparate data sources make it very difficult to keep everyone on the same page and hinder collaboration and productivity, especially as an organization grows. Staff spend time searching for documents and potentially repeating work, as there is no place to look for up-to-date information on all aspects of the business for them. This also makes it difficult to see the exact cause and effect of developments affecting your business.
An ERP system solves this problem by collecting information in a central database to provide managers and employees with cross-departmental visibility. At the same time, it eliminates the problems that come with conflicting data sources and empowers them to analyze different scenarios, discover process improvements and realize huge productivity gains. This means cost savings and better productivity as people spend less time searching for the data they need.
Tailored to meet the needs of an individual business, ERP software yields big gains, making these systems a critical tool for companies of all sizes and industries. Many of the world’s best-known and most successful companies have been relying on ERP for the past quarter century. Now this software can be configured and priced to meet the needs of businesses of any size.

Enterprise resource planning (a term coined by research firm Gartner in 1990) can be a confusing concept because ERP is not a stand-alone application. While ERP is a category of business software, ERP systems are made up of different modules, each meeting specific business needs. For example, product-based companies often have modules for accounting, inventory and order management, customer relationship management (CRM), and manufacturing if they are producing or assembling products. Service businesses may turn to modules for accounting, project management, professional service automation, and CRM.
Magento Integration With Erp
Each module pulls information from the central database, which is an important component of the ERP system, and transmits the information to this database. This shared repository provides visibility across all departments, enabling leaders to evaluate and compare business performance across different areas and understand the full impact of decisions. It also supports other ERP benefits such as process automation, improved internal controls, and smarter business intelligence.
There are two basic approaches to building an ERP system. The first is to purchase software from different vendors that can perform each of these core business functions such as accounting, sales, inventory, and production. These solutions are then integrated with a central database (ERP). The second is to buy all the modules you need from the ERP vendor and avoid integrations as the applications are already designed to work together.
Getting most or all of the ERP modules you need from a single vendor is the best option for the vast majority of businesses because of its simplicity. Integrating these disparate systems is often complex and requires a large IT staff or IT services partner, so it doesn’t make sense for most small to midsize organizations. Once these integrations are in place, they require ongoing maintenance.
A unified platform, on the other hand, offers native integrations between modules and a common user interface as users move between modules. This allows for easier ERP implementation. Information flows easily between modules to give decision makers a comprehensive view of the company.
Seriously, Excel Is Not An Erp
ERP systems have become the tableau of businesses that want to use resources wisely. They can help leaders reallocate human and financial capital or create more efficient core business processes that save money without sacrificing quality or performance.
ERP is also an advantage when it comes to planning and coordination. Employees can view current inventory and customer orders in detail, then compare purchase orders from suppliers and estimated future demand. If necessary, they can make adjustments to resolve the issues. ERP software improves communication and collaboration as employees can check the status of other departments to guide their own decisions.
As a comprehensive data source, an ERP system also provides a range of reports and analytics that can make a difference to a business. Turning large amounts of information into tables and graphs that clearly show trends and help model possible outcomes is an ERP capability that managers find invaluable.

ERP systems operate using a defined, standard data structure. Information entered by a department is instantly available to authorized users across the enterprise. This uniform structure helps everyone stay on the same page. For example, let’s say a local food distribution chain has multiple locations that often share inventory and staff. The quality, sales and employee data coming from these sites are formatted to show from which location they are fed into the ERP system.
Best & Fastest Growing Erp Software
Real-time data is then processed into business processes and workflows across departments. Leaders can see if a location is significantly better at preventing disruptions than a sister location in several cities, and operations can ensure staffing levels match traffic patterns as they work to find out why. Finance can compare sales to leases to help managers decide whether to consolidate.
ERP systems provide the most value when a company has modules for each core business function and provides timely, accurate data entry. And the more stakeholders have access, the better.
When a company uses business systems from multiple vendors, integrations are often possible to allow data to flow automatically into ERP. This real-time data can then be used in the ERP cloud server to leverage any process or workflow.
ERP modules are available to assist with almost every core business function, from finance to supply chain to human resources.
Erp Abbreviation Enterprise Resource Planning Text Stock Photo 1129475006
ERP consists of a number of different modules – functional packages tailored to different aspects of the business, including back and front office roles. This goes beyond finance and other core functions such as supply chain management and customer communication. Here is a quick overview of the most used ERP modules:
Finance. The foundation of almost every ERP system, a finance module manages the general ledger and all financial data. It monitors every transaction including accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) and manages reconciliations and financial reporting.
Supply. The procurement module manages purchases, whether raw materials or finished goods. HE

Sap erp stands for, what erp system stands for, erp stands for singapore, erp stands for, erp system stands for, erp stands for in computer, erp stands for finance, what does erp stands for, erp stands, erp stands for software, what stands for erp, erp stands for enterprise resource planning